Photographs of Incrediable India
Dal lake Jama Masjid Mosque Kashmir houseboats Pahalgam Shikaras Srinagar Srinagar Markets
Kerala
Cheena vala Kochi Mattancherry-Palace
Maharashtra
Amber Fort Camel-Safari Gadi Sagar Lake Jaigarh Fort Jaipur Albert Hall
Jaipur City Palace Jaipur Hawa Mahal Jaisalmer Jaisalmer Jain
Jaswant Thada Jodhpur Mehrangarh Fort Nahargarh Fort
Ranakpur Jain Temple Thar Desert Udaipur to Ranakpur
Tamil Nadu
Meenakshi Temple Murugan Temple Alagar Kovil Temple
Agra Fort Akbars Tomb Ta Mahal
Mixed Images
India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: भारत गणराज्य Bhārat Ganarājya; see also other Indian languages), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the south, the Arabian Sea on the west, and the Bay of Bengal on the east, India has a coastline of 7,517 kilometers (4,671 mi). It is bordered by Pakistan to the west; People's Republic of China (PRC), Nepal, and Bhutan to the north; and Bangladesh and Myanmar to the east. India is in the vicinity of Sri Lanka, the Maldives, and Indonesia in the Indian Ocean.
Home to the Indus Valley Civilization and a region of historic trade routes and vast empires, the Indian subcontinent was identified with its commercial and cultural wealth for much of its long history. Four major world religions, Hinduism, Buddhism, Jainism and Sikhism originated there, while Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Christianity and Islam arrived in the first millennium CE and shaped the region's diverse culture. Gradually annexed by the British East India Company from the early eighteenth century and colonised by the United Kingdom from the mid-nineteenth century, India became an independent nation in 1947 after a struggle for independence that was marked by widespread nonviolent resistance.
India is a republic consisting of 28 states and seven union territories with a parliamentary system of democracy. India maintains the world's third largest army with the ninth largest defense budget. It is a nuclear weapons state and a potential superpower. It has the world's twelfth largest economy at market exchange rates and the fourth largest in purchasing power. Economic reforms since 1991 have transformed it into one of the fastest growing economies. A pluralistic, multilingual, and multiethnic society, India is also home to a diversity of wildlife in a variety of protected habitats; however, it still suffers from high levels of poverty, illiteracy, and malnutrition.
Etymology
The name India is derived from Indus, which is derived from the Old Persian word Hindu, from Sanskrit Sindhu, the historic local appellation for the Indus River. The ancient Greeks referred to the Indians as Indoi (Ινδοί), the people of the Indus. The Constitution of India and common usage in various Indian languages also recognise Bharat (hi-Bharat.ogg pronunciation as an official name of equal status. Hindustan, which is the Persian word for “Land of the Hindus” and historically referred to northern India, is also occasionally used as a synonym for all of India.
History
Stone Age rock shelters with paintings at the Bhimbetka rock shelters in Madhya Pradesh are the earliest known traces of human life in India. The first known permanent settlements appeared over 9,000 years ago and gradually developed into the Indus Valley Civilisation, dating back to 3300 BCE in western India. It was followed by the Vedic period, which laid the foundations of Hinduism and other cultural aspects of early Indian society, and ended in the 500s BCE. From around 550 BCE, many independent kingdoms and republics known as the Mahajanapadas were established across the country.
In the third century BCE, most of South Asia was united into the Maurya Empire by Chandragupta Maurya and flourished under Ashoka the Great. From the third century CE, the Gupta dynasty oversaw the period referred to as ancient "India's Golden Age." Empires in Southern India included those of the Chalukyas, the Cholas and the Vijayanagara Empire. Science, engineering, art, literature, astronomy, and philosophy flourished under the patronage of these kings.
Following invasions from Central Asia between the 10th and 12th centuries, much of North India came under the rule of the Delhi Sultanate and later the Mughal Empire. Under the rule of Akbar the Great, India enjoyed much cultural and economic progress as well as religious harmony. Mughal emperors gradually expanded their empires to cover large parts of the subcontinent. However, in North-Eastern India, the dominant power was the Ahom kingdom of Assam, among the few kingdoms to have resisted Mughal subjugation. The first major threat to Mughal imperial power came from a Hindu state known as the Maratha confederacy, that dominated much of India in the mid-18th century.
From the 16th century, European powers such as Portugal, the Netherlands, France, and the United Kingdom established trading posts and later took advantage of internal conflicts to establish colonies in the country. By 1856, most of India was under the control of the British East India Company. A year later, a nationwide insurrection of rebelling military units and kingdoms, known as India's First War of Independence or the Sepoy Mutiny, seriously challenged the Company's control but eventually failed. As a result of the instability, India was brought under the direct rule of the British Crown.
In the 20th century, a nationwide struggle for independence was launched by the Indian National Congress and other political organisations. Indian leader Mahatma Gandhi led millions of people in national campaigns of non-violent civil disobedience. On 15 August 1947, India gained independence from British rule, but at the same time Muslim-majority areas were partitioned to form a separate state of Pakistan. On 26 January 1950, India became a republic and a new constitution came into effect.
Since independence, India has faced challenges from religious violence, casteism, naxalism, terrorism and regional separatist insurgencies, especially in Jammu and Kashmir and Northeast India. Since the 1990s terrorist attacks have affected many Indian cities. India has unresolved territorial disputes with P. R. China, which in 1962 escalated into the Sino-Indian War; and with Pakistan, which resulted in wars in 1947, 1965, 1971 and 1999. India is a founding member of the United Nations (as British India) and the Non-Aligned Movement. In 1974, India conducted an underground nuclear test and five more tests in 1998, making India a nuclear state. Beginning in 1991, significant economic reforms have transformed India into one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, increasing its global clout.
Government
The Constitution of India, the longest and the most exhaustive constitution of any independent nation in the world, came into force on 26 January, 1950. The preamble of the constitution defines India as a sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic republic. India has a bicameral parliament operating under a Westminster-style parliamentary system. Its form of government was traditionally described as being 'quasi-federal' with a strong centre and weaker states, but it has grown increasingly federal since the late 1990s as a result of political, economic and social changes.
The President of India is the head of state elected indirectly by an electoral college for a five-year term. The Prime Minister is the head of government and exercises most executive powers. Appointed by the President, the Prime Minister is by convention supported by the party or political alliance holding the majority of seats in the lower house of Parliament. The executive branch consists of the President, Vice-President, and the Council of Ministers (the Cabinet being its executive committee) headed by the Prime Minister. Any minister holding a portfolio must be a member of either house of parliament. In the Indian parliamentary system, the executive is subordinate to the legislature, with the Prime Minister and his Council being directly responsible to the lower house of the Parliament.
The Legislature of India is the bicameral Parliament, which consists of the upper house called the Rajya Sabha (Council of States) and the lower house called the Lok Sabha (House of People). The Rajya Sabha, a permanent body, has 245 members serving staggered six year terms. Most are elected indirectly by the state and territorial legislatures in proportion to the state's population. 543 of the Lok Sabha's 545 members are directly elected by popular vote to represent individual constituencies for five year terms. The other two members are nominated by the President from the Anglo-Indian community if the President is of the opinion that the community is not adequately represented.
India has a unitary three-tier judiciary, consisting of the Supreme Court, headed by the Chief Justice of India, twenty-one High Courts, and a large number of trial courts. The Supreme Court has original jurisdiction over cases involving fundamental rights and over disputes between states and the Centre, and appellate jurisdiction over the High Courts. It is judicially independent, and has the power to declare the law and to strike down Union or State laws which contravene the Constitution. The role as the ultimate interpreter of the Constitution is one of the most important functions of the Supreme Court.
Administrative divisions
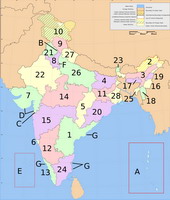
India is a federal republic of twenty-eight states and seven Union Territories. All states, and the two union territories of Puducherry and the National Capital Territory of Delhi have elected governments. The other five union territories have centrally appointed administrators and hence are under direct rule of the President. In 1956, under the States Reorganisation Act, states were formed on a linguistic basis. Since then, this structure has remained largely unchanged. Each state or union territory is further divided into 610 districts for basic governance and administration. The districts in turn are further divided into tehsils and eventually into villages.
Administrative divisions of India, including 28 states and 7 union territories.
States:
1. Andhra Pradesh
2. Arunachal Pradesh
3. Assam
4. Bihar
5. Chhattisgarh
6. Goa
7. Gujarat
8. Haryana
9. Himachal Pradesh
10. Jammu and Kashmir
11. Jharkhand
12. Karnataka
13. Kerala
14. Madhya Pradesh
15. Maharashtra
16. Manipur
17. Meghalaya
18. Mizoram
19. Nagaland
20. Orissa
21. Punjab
22. Rajasthan
23. Sikkim
24. Tamil Nadu
25. Tripura
26. Uttar Pradesh
27. Uttarakhand
28. West BengalUnion Territories:
1. Andaman and Nicobar Islands
2. Chandigarh
3. Dadra and Nagar Haveli
4. Daman and Diu
5. Lakshadweep
6. National Capital Territory of Delhi
7. Puducherry
Politics
India is the most populous democracy in the world. For most of the years since independence, the federal government has been led by the Indian National Congress (INC). Politics in the states have been dominated by several national parties including the INC, the Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP), the Communist Party of India (Marxist) (CPI(M)) and various regional parties. From 1950 to 1990, barring two brief periods, the INC enjoyed a parliamentary majority. The INC was out of power between 1977 and 1980, when the Janata Party won the election owing to public discontent with the state of emergency declared by the then Prime Minister Indira Gandhi. In 1989, a Janata Dal-led National Front coalition in alliance with the Left Front coalition won the elections but managed to stay in power for only two years. As the 1991 elections gave no political party a majority, the INC formed a minority government under Prime Minister P.V. Narasimha Rao and was able to complete its five-year term.
The years 1996–1998 were a period of turmoil in the federal government with several short-lived alliances holding sway. The BJP formed a government briefly in 1996, followed by the United Front coalition that excluded both the BJP and the INC. In 1998, the BJP formed the National Democratic Alliance (NDA) with several other parties and became the first non-Congress government to complete a full five-year term. In the 2004 Indian elections, the INC won the largest number of Lok Sabha seats and formed a government with a coalition called the United Progressive Alliance (UPA), supported by various Left-leaning parties and members opposed to the BJP.
Foreign relations and military
Since its independence in 1947, India has maintained cordial relationships with most nations. It took a leading role in the 1950s by advocating the independence of European colonies in Africa and Asia. India was involved in two brief military interventions in neighboring countries - Indian Peace Keeping Force in Sri Lanka and Operation Cactus in Maldives. India is a member of the Commonwealth of Nations and a founding member of the Non-Aligned Movement. After the Sino-Indian War and the Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, India's relationship with the Soviet Union warmed at the expense of ties with the United States and continued to remain so until the end of the Cold War. India has fought three wars with Pakistan, primarily over Kashmir but it also facilitated the creation of Bangladesh in 1971. Additional skirmishes have taken place between the two nations particularly in 1984 over the Siachen Glacier and in 1999 over Kargil.
In recent years, India has played an influential role in the SAARC, and the WTO. India has provided as many as 55,000 Indian military and police personnel to serve in thirty-five UN peace keeping operations across four continents. Despite criticism and military sanctions, India has consistently refused to sign the CTBT and the NPT, preferring instead to maintain sovereignty over its nuclear program. Recent overtures by the Indian government have strengthened relations with the United States, P. R. China and Pakistan. In the economic sphere, India has close relationships with other developing nations in South America, Asia and Africa.
India maintains the third-largest military force in the world, which consists of the Indian Army, Navy and Air Force. Auxiliary forces such as the Paramilitary Forces, the Coast Guard, and the Strategic Forces Command also come under the military's purview. The President of India is the supreme commander of the Indian armed forces. India maintains close defence cooperation with Russia, France and Israel, who are the chief suppliers of arms. The Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) has overseen the indigenous development of sophisticated arms and military equipment, including ballistic missiles, fighter aircrafts and main battle tanks, to reduce India's dependence on foreign imports. India became a nuclear power in 1974 after conducting an initial nuclear test, Operation Smiling Buddha and further underground testing in 1998. India maintains a "no first use" nuclear policy. On 10 October, 2008 Indo-US civilian nuclear agreement was signed, prior to which India received the IAEA and NSG waivers, ending restrictions on nuclear technology commerce with which India became de facto sixth nuclear power in world.
Geography
India, the major portion of the Indian subcontinent, sits atop the Indian tectonic plate, a minor plate within the Indo-Australian Plate.
India's defining geological processes commenced seventy-five million years ago, when the Indian subcontinent, then part of the southern supercontinent Gondwana, began a northeastwards drift—lasting fifty million years—across the then unformed Indian Ocean. The subcontinent's subsequent collision with the Eurasian Plate and subduction under it, gave rise to the Himalayas, the planet's highest mountains, which now abut India in the north and the north-east. In the former seabed immediately south of the emerging Himalayas, plate movement created a vast trough, which, having gradually been filled with river-borne sediment, now forms the Indo-Gangetic Plain. To the west of this plain, and cut off from it by the Aravalli Range, lies the Thar Desert. The original Indian plate now survives as peninsular India, the oldest and geologically most stable part of India, and extending as far north as the Satpura and Vindhya ranges in central India. These parallel ranges run from the Arabian Sea coast in Gujarat in the west to the coal-rich Chota Nagpur Plateau in Jharkhand in the east. To their south, the remaining peninsular landmass, the Deccan Plateau, is flanked on the left and right by the coastal ranges, Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats respectively; the plateau contains the oldest rock formations in India, some over one billion years old. Constituted in such fashion, India lies to the north of the equator between 6°44' and 35°30' north latitude and 68°7' and 97°25' east longitude.
India's coast is 7,517 kilometers (4,671 mi) long; of this distance, 5,423 kilometers (3,370 mi) belong to peninsular India, and 2,094 kilometers (1,301 mi) to the Andaman, Nicobar, and Lakshadweep Islands. According to the Indian naval hydrographic charts, the mainland coast consists of the following: 43% sandy beaches, 11% rocky coast including cliffs, and 46% mudflats or marshy coast.
Tso Kiagar Lake at Ladakh on the Himalayas
Major Himalayan-origin rivers that substantially flow through India include the Ganges and the Brahmaputra, both of which drain into the Bay of Bengal. Important tributaries of the Ganges include the Yamuna and the Kosi, whose extremely low gradient causes disastrous floods every year. Major peninsular rivers whose steeper gradients prevent their waters from flooding include the Godavari, the Mahanadi, the Kaveri, and the Krishna, which also drain into the Bay of Bengal; and the Narmada and the Tapti, which drain into the Arabian Sea. Among notable coastal features of India are the marshy Rann of Kutch in western India, and the alluvial Sundarbans delta, which India shares with Bangladesh. India has two archipelagos: the Lakshadweep, coral atolls off India's south-western coast; and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, a volcanic chain in the Andaman Sea.
India's climate is strongly influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert, both of which drive the monsoons. The Himalayas prevent cold Central Asian katabatic winds from blowing in, keeping the bulk of the Indian subcontinent warmer than most locations at similar latitudes. The Thar Desert plays a crucial role in attracting the moisture-laden southwest summer monsoon winds that, between June and October, provide the majority of India's rainfall. Four major climatic groupings predominate in India: tropical wet, tropical dry, subtropical humid, and montane.
Flora and fauna
India, which lies within the Indomalaya ecozone, displays significant biodiversity. One of eighteen megadiverse countries, it is home to 7.6% of all mammalian, 12.6% of all avian, 6.2% of all reptilian, 4.4% of all amphibian, 11.7% of all fish, and 6.0% of all flowering plant species. Many ecoregions, such as the shola forests, exhibit extremely high rates of endemism; overall, 33% of Indian plant species are endemic. India's forest cover ranges from the tropical rainforest of the Andaman Islands, Western Ghats, and North-East India to the coniferous forest of the Himalaya. Between these extremes lie the sal-dominated moist deciduous forest of eastern India; the teak-dominated dry deciduous forest of central and southern India; and the babul-dominated thorn forest of the central Deccan and western Gangetic plain. Important Indian trees include the medicinal neem, widely used in rural Indian herbal remedies. The pipal fig tree, shown on the seals of Mohenjo-daro, shaded Gautama Buddha as he sought enlightenment.
Many Indian species are descendants of taxa originating in Gondwana, to which India originally belonged. Peninsular India's subsequent movement towards, and collision with, the Laurasian landmass set off a mass exchange of species. However, volcanism and climatic changes 20 million years ago caused the extinction of many endemic Indian forms. Soon thereafter, mammals entered India from Asia through two zoogeographical passes on either side of the emerging Himalaya. Consequently, among Indian species, only 12.6% of mammals and 4.5% of birds are endemic, contrasting with 45.8% of reptiles and 55.8% of amphibians. Notable endemics are the Nilgiri leaf monkey and the brown and carmine Beddome's toad of the Western Ghats. India contains 172, or 2.9%, of IUCN-designated threatened species. These include the Asiatic Lion, the Bengal Tiger, and the Indian white-rumped vulture, which suffered a near-extinction from ingesting the carrion of diclofenac-treated cattle.
In recent decades, human encroachment has posed a threat to India's wildlife; in response, the system of national parks and protected areas, first established in 1935, was substantially expanded. In 1972, India enacted the Wildlife Protection Act and Project Tiger to safeguard crucial habitat; in addition, the Forest Conservation Act was enacted in 1980. Along with more than five hundred wildlife sanctuaries, India hosts thirteen biosphere reserves, four of which are part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves; twenty-five wetlands are registered under the Ramsar Convention.
Economy
For an entire generation from the 1950s until the 1980s, India followed socialist-inspired policies. The economy was shackled by extensive regulation, protectionism, and public ownership, leading to pervasive corruption and slow growth. Since 1991, the nation has moved towards a market-based system. The policy change in 1991 came after an acute balance of payments crisis, and the emphasis since then has been to use foreign trade and foreign investment as integral parts of India's economy.
With an average annual GDP growth rate of 5.8% for the past two decades, the economy is among the fastest growing in the world. It has the world's second largest labour force, with 516.3 million people. In terms of output, the agricultural sector accounts for 28% of GDP; the service and industrial sectors make up 54% and 18% respectively. Major agricultural products include rice, wheat, oilseed, cotton, jute, tea, sugarcane, potatoes; cattle, water buffalo, sheep, goats, poultry; fish. Major industries include textiles, chemicals, food processing, steel, transportation equipment, cement, mining, petroleum, machinery, software. India's trade has reached a relatively moderate share 24% of GDP in 2006, up from 6% in 1985. India's share of world trade has reached 1%. Major exports include petroleum products, textile goods, gems and jewelry, software, engineering goods, chemicals, leather manufactures. Major imports include crude oil, machinery, gems, fertilizer, chemicals.
India's GDP is US$1.089 trillion, which makes it the twelfth-largest economy in the world or fourth largest by purchasing power adjusted exchange rates. India's nominal per capita income US$977 is ranked 128th in the world. In the late 2000s, India's economic growth has averaged 7½% a year, which will double the average income in a decade.
India remains one of the poorest countries in the world. The percentage of people living below the new international poverty line $1.25 a day (PPP, in nominal terms Rs 21.6 a day in urban areas and Rs 14.3 in rural areas in 2005) decreased from 60% in 1981 to 42% in 2005. 85.7% of the population was living on less than $2.50 (PPP) a day in 2005, compared with 80.5% for Sub-Saharan Africa. Even though India has avoided famines in recent decades, half of children are underweight, one of the highest rates in the world and nearly double the rate of Sub-Saharan Africa.
Ongoing reforms are watched closely as India could become potentially important for the global economy. A Goldman Sachs report predicts that "from 2007 to 2020, India’s GDP per capita will quadruple,’ and that the Indian economy will surpass the United States by 2043, but India "will remain a low-income country for several decades, with per capita incomes well below its other BRIC peers. But if it can fulfill its growth potential, it can become a motor for the world economy, and a key contributor to generating spending growth‘. Although the Indian economy has grown steadily over the last two decades; its growth has been uneven when comparing different social groups, economic groups, geographic regions, and rural and urban areas. World Bank suggests that the most important priorities are public sector reform, infrastructure, agricultural and rural development, removal of labor regulations, reforms in lagging states, and HIV/AIDS.
Demographics
With an estimated population of 1.15 billion, representing 17% of the world population, India is the world's second most populous country. The last 50 years have seen a rapid increase in population due to medical advances and massive increase in agricultural productivity made by the green revolution. Almost 70% of Indians reside in rural areas, although in recent decades migration to larger cities has led to a dramatic increase in the country's urban population. India's largest cities are Mumbai (formerly Bombay), Delhi, Kolkata (formerly Calcutta), Chennai (formerly Madras), Bengaluru (formerly Bangalore), Hyderabad and Ahmedabad.
India is the most culturally, linguistically and genetically diverse geographical entity after the African continent. India is home to two major linguistic families: Indo-Aryan (spoken by about 74% of the population) and Dravidian (spoken by about 24%). Other languages spoken in India come from the Austro-Asiatic and Tibeto-Burman linguistic families. Hindi, with the largest number of speakers, is the official language of the union. English, which is extensively used in business and administration, has the status of a 'subsidiary official language;' it is also important in education, especially as a medium of higher education. In addition, every state and union territory has its own official languages, and the constitution also recognises in particular 21 other languages that are either abundantly spoken or have classical status. While Sanskrit and Tamil have been studied as classical languages for many years, the Government of India, using its own criteria, has also accorded classical language status to Kannada and Telugu. The number of dialects in India is as high as 1,652.
Over 800 million Indians (80.5%) are Hindu. Other religious groups include Muslims (13.4%), Christians (2.3%), Sikhs (1.9%), Buddhists (0.8%), Jains (0.4%), Jews, Zoroastrians, Bahá'ís and others. Tribals constitute 8.1% of the population.
India's literacy rate is 64.8% (53.7% for females and 75.3% for males). The state of Kerala has the highest literacy rate (91%); Bihar has the lowest (47%). The national human sex ratio is 944 females per 1,000 males. India's median age is 24.9, and the population growth rate of 1.38% per annum; there are 22.01 births per 1,000 people per year.
Culture
India's culture is marked by a high degree of syncretism and cultural pluralism. It has managed to preserve established traditions while absorbing new customs, traditions, and ideas from invaders and immigrants and spreading its cultural influence to other parts of Asia.
Traditional Indian society is defined by relatively strict social hierarchy. The Indian caste system describes the social stratification and social restrictions in the Indian subcontinent, in which social classes are defined by thousands of endogamous hereditary groups, often termed as jātis or castes.
Traditional Indian family values are highly respected, and multi-generational patriarchal joint families have been the norm, although nuclear family are becoming common in urban areas. An overwhelming majority of Indians have their marriages arranged by their parents and other respected family-members, with the consent of the bride and groom. The marriage is thought to be for life, and the divorce rate is extremely low. Child marriage is still a common practice, with half of women in India marry before the legal age of 18.
Indian cuisine is characterized by a wide variety of regional styles and sophisticated use of herbs and spices. The staple foods in the region are rice (especially in the south and the east) and wheat (predominantly in the north). Spices originally native to the Indian subcontinent that are now consumed world wide include black pepper; in contrast, hot chili peppers, popular across India, were introduced by the Portuguese.
Traditional Indian dress varies across the regions in its colours and styles and depends on various factors, including climate. Popular styles of dress include draped garments such as sari for women and dhoti or lungi for men; in addition, stitched clothes such as salwar kameez for women and kurta-pyjama and European-style trousers and shirts for men, are also popular.
Many Indian festivals are religious in origin, although several are celebrated irrespective of caste and creed. Some popular festivals are Diwali, Ganesh Chaturthi, Ugadi, Thai Pongal, Holi, Onam, Vijayadasami, Durga Puja, Eid ul-Fitr, Bakr-Id, Christmas, Buddha Jayanti and Vaisakhi. India has three national holidays. Other sets of holidays, varying between nine and twelve, are officially observed in individual states. Religious practices are an integral part of everyday life and are a very public affair.
Indian architecture is one area that represents the diversity of Indian culture. Much of it, including notable monuments such as the Taj Mahal and other examples of Mughal architecture and South Indian architecture, comprises a blend of ancient and varied local traditions from several parts of the country and abroad. Vernacular architecture also displays notable regional variation.
Indian music covers a wide range of traditions and regional styles. Classical music largely encompasses the two genres – North Indian Hindustani, South Indian Carnatic traditions and their various offshoots in the form of regional folk music. Regionalised forms of popular music include filmi and folk music; the syncretic tradition of the bauls is a well-known form of the latter.
Indian dance too has diverse folk and classical forms. Among the well-known folk dances are the bhangra of the Punjab, the bihu of Assam, the chhau of West Bengal, Jharkhand and sambalpuri of Orissa and the ghoomar of Rajasthan. Eight dance forms, many with narrative forms and mythological elements, have been accorded classical dance status by India's National Academy of Music, Dance, and Drama. These are: bharatanatyam of the state of Tamil Nadu, kathak of Uttar Pradesh, kathakali and mohiniyattam of Kerala, kuchipudi of Andhra Pradesh, manipuri of Manipur, odissi of Orissa and the sattriya of Assam.
Theatre in India often incorporates music, dance, and improvised or written dialogue. Often based on Hindu mythology, but also borrowing from medieval romances, and news of social and political events, Indian theatre includes the bhavai of state of Gujarat, the jatra of West Bengal, the nautanki and ramlila of North India, the tamasha of Maharashtra, the burrakatha of Andhra Pradesh, the terukkuttu of Tamil Nadu, and the yakshagana of Karnataka.
The Indian film industry is the largest in the world. Bollywood, based in Mumbai, makes commercial Hindi films and is the most prolific film industry in the world. Established traditions also exist in Bengali, Kannada, Malayalam, Marathi, Tamil, and Telugu language cinemas.
The earliest works of Indian literature were transmitted orally and only later written down. These included works of Sanskrit literature – such as the early Vedas, the epics Mahābhārata and Ramayana, the drama Abhijñānaśākuntalam (The Recognition of Śakuntalā), and poetry such as the Mahākāvya – and the Tamil language Sangam literature. Among Indian writers of the modern era active in Indian languages or English, Rabindranath Tagore won the Nobel Prize in 1913.
Sports
India's official national sport is field hockey, administered by the Indian Hockey Federation. The Indian field hockey team won the 1975 Men's Hockey World Cup and 8 gold, 1 silver and 2 bronze medals at the Olympic games. However, cricket is the most popular sport; the India national cricket team won the 1983 Cricket World Cup and the 2007 ICC World Twenty20, and shared the 2002 ICC Champions Trophy with Sri Lanka. Cricket in India is administered by the Board of Control for Cricket in India, and domestic competitions include the Ranji Trophy, the Duleep Trophy, the Deodhar Trophy, the Irani Trophy and the Challenger Series. In addition Indian cricket league and Indian premier league organize Twenty20 competitions.
Tennis has become increasingly popular, owing to the victories of the India Davis Cup team. Association football is also a popular sport in northeast India, West Bengal, Goa and Kerala. The Indian national football team has won the South Asian Football Federation Cup several times. Chess, commonly held to have originated in India, is also gaining popularity with the rise in the number of Indian Grandmasters. Traditional sports include kabaddi, kho kho, and gilli-danda, which are played nationwide. India is also home to the ancient martial arts, Kalarippayattu and Varma Kalai.
The Rajiv Gandhi Khel Ratna and the Arjuna Award are India's highest awards for achievements in sports, while the Dronacharya Award is awarded for excellence in coaching. India hosted or co-hosted the 1951 and the 1982 Asian Games, the 1987 and 1996 Cricket World Cup. It is also scheduled to host the 2010 Commonwealth Games and the 2011 Cricket World Cup.
Web Reference: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/India
India is the world's largest democracy, and one of the oldest and most successful in Asia. It is also the world's second most populous country, with a great variety of peoples, several major religious groupings, and 700 languages. In the 50 years since independence, in 1947, it has on the whole managed humanely and responsibly where other countries in the region have become totalitarian, or succumbed to military rule. However, there are major conflicts-there have been three wars with Pakistan alone. The dispute with Pakistan over Kashmir remains unresolved. The caste system also produces endemic injustice. Millions live in desperate poverty. But Indians can change their government democratically by going to the polls, and the lot of most people has slowly but steadily improved. After a long period of state regulation of industry, barriers to outside investment, and a maze of protectionist controls, the country has begun to open its economy to the outside world. Population growth, however, with a figure of 2% on a base of almost a billion, tends to cancel out the nation's gains.
Physical features and land use North to south, India can be divided into three regions: the Himalayas and their foothills; the Indo-Gangetic Plain; and the Deccan Plateau. From the northern most border, the heavily glaciated terrain of the Himalayas-the world's highest mountains cover 15% of the total surface area. The name Himalaya comes from the Nepalese him (snows) and alya (home of), the mountains being revered as the home of the gods. The peaks rise to elevations of over 7,000 m (23,000 ft) in the Ladakh and Karakoram ranges. The western highlands towards the Karakoram mountains are harsh, dry, and inhabited only by small communities of herds people. At lower altitudes alpine meadows are grazed by the sheep of migratory pastoralists who arrive in the summer with their flocks. Lower still, rice terraces and orchards are found in the Vale of Kashmir.
The eastern highlands of northern Assam are markedly different. They are much wetter-this is where rhododendrons and magnolias grow wild and where terraced hills support rice, buckwheat, and barley. The climate of the high plateau of Meghalaya, separated from the Himalayas by the valley of the Brahmaputra, is damp and cool. On its southern flanks, Cherrapunji has one of the world's highest rainfalls, averaging 10,798 mm (421.1 in) per year.
South of the northern mountains lie the terai or foothill plains; still further south the main plains region of India stretches from the western coastal lowlands, in a northern arc past the Thar Desert and down the Gangetic Plain to the mouth of the Hooghly on the Bay of Bengal. In the northwest the Punjab and Halyana farmers grow winter wheat, summer rice, cotton, and sugarcane, with sorghum in the drier areas. On the lowlands of the central part of Uttar Pradesh millet and sorghum are preferred to wheat and rice. Jute is cultivated where the Ganges enters the distributary system of the delta, while mangrove swamps line the marine margins of the delta itself.
The Thar Desert in the northwest contains a broad area of dunes in Rajasthan; southwest of this lie the cotton-growing lands of Gujarat, which includes the low peninsular plateau of Kathiawar between the Gulf of Khambhat and the Gulf of Khachchh, not far from the Pakistan border. The Vindya Range east of the Gulf of Khamhhat separates the Indo-Gangetic Plain from peninsular India and the Deccan Plateau. This plateau contains some of the world's oldest rocks, large tracts being covered with later basalt flows. The Western edge of the plateau is defined by the mountain chain of the Western Ghats. At the foot of these mountains lies a coastal plain with coconut groves, fishing villages, rice fields, and tapioca plantations. On the plateau itself the main crops are millet and pulses.
History
Of India's various civilizations, the earliest developed in the Indus Valley (c,2600 BC) and in the Ganges Valley (c.1500 BC). At this time, the subcontinent was mainly peopled by ethnic Dravidians. It is thought that the Indus civilization succumbed to an invasion of Sanskrit speaking Aryan peoples who introduced the caste system, a scheme of social division that is fundamental in Indian life. Another important early civilization was the Maurya, which under Ashoka, who reigned from 273 to 232 BC, came to dominate the subcontinent. Later, a succession of Arab, Turkish, and Mongol influences led to the founding in 1526 of the Mogul Empire, which under Akbar (1542-1605) was extended throughout most of northern India and part of the Deccan. It was during the time of Mogul rule that the Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan, The British effectively controlled India from 1805, during the nineteenth century introducing a civil service and a code of law which have profoundly shaped the nation since that time. With the coming of independence in 1947, the division between Hindus and Muslims resulted in the violent and tumultuous partition of the country into India and Pakistan. This first major division to split the country indicates that the most serious rifts within Indian society tend to be religious. In recent years the Sikhs of the Punjah have also been agitating for independence.
Economy
Once essentially rural, India's economy is now a mix of village farming, modern agriculture, handicrafts, a variety of modern industries, and innumerable support services. During the 1980s economic growth allowed a marked increase in real per capita private consumption. Since 1991 production, trade, and investment reforms have provided new, opportunities for Indian business and some 200 million middle class consumers.
Among the nation's strengths is a home market of some 900 million, along with a workforce that includes many who are highly skilled, including those trained in high-tech areas such as computer programming. The textile sector is highly efficient. There has been a massive rise in foreign investment as the country has opened up to foreign competition. The downside of this situation is a sizeable budget deficit along with high defense spending, (including that for nuclear weapons) because of the long running and continuing conflict with Pakistan. Other negative features include an absence of even elementary social services, poor roads, inadequate port facilities, and an antiquated telecommunications system.
STATES AND CAPITALS
Andhra Pradesh: Hyderabad
Arunachal Pradesh: Ita nagar
Assam: Dispur
Bihar: Patna
Goa: Panaji
Gujarat: Gandhinagar
Haryana: Chandigarh
Himachal Pradesh: Simla
Jammu and Kashmir: Srinagar (summer) Jammu (winter)
Karnataka: Bangalore
Kerala: Trivandrum
Madhya Pradesh: Bhopal
Maharashtra: Mumbai (Bombay)
Manipur: Imphal
Meghalaya: Shillong
Mizoram: Aizawi
Nagaland: Kohima
Orissa: Bhubaneswar
Punjab: Chandigarh
Rajastan: ]aipur
Sikkim: Gangtok
Tamil Nadu: Madras
Tripura: Agartala
Uttar Pradesh: Lucknow
West Bengal: Calcutta
UNION TERRITORIES
Andaman and Nicobar Islands: Port Blair
Chandigarh: Chandigarh
Dadra and Nagar Haveli:
Silvassa Daman and Diu: Daman
Delhi: Delhi
Lakshadweep: Kavaratti
Pondicherry: Pondicherry
Fact File
OFFICIAL NAME Republic of India
FORM OF GOVERNMENT Federal republic with two legislative bodies (Council of States and People's Assembly)
CAPITAL New Delhi
AREA 3,287,590 sq km (1,269,338 sq miles) TIME ZONE GMT + 5.5 hours
POPULATION 999,826,804
PROJECTED POPULATION 2005 1,096,929,474
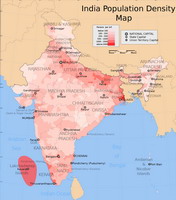
POPULATION DENSITY 304.1 per sq km (787.7 per sq mile)
LIFE EXPECTANCY 63.4
INFANT MORTALITY (PER 1,000) 60.8
OFFICIAL LANGUAGES Hindi, Bengali, Telugu, Marathi, Tamil, Urdu, Gujarati, Malayalam, Kannada, Oriya, Punjabi, Assamese, Kashmiri, Sind hi, Sanskrit, English
OTHER LANGUAGES Hindustani, about 700 indigenous languages
LITERACY RATE 51.2%
RELIGIONS Hindu 80%, Muslim 14%, Christian 2.4%, Sikh 2%, Buddhist 0.7%, Jain 0.5%, other 0.4%
ETHNIC GROUPS Indo-Aryan 72%, Dravidian 25%, Mongoloid and other 3%
CURRENCY Indian rupee
ECONOMY Agriculture 63%, services 26%, industry 11%
GNP PER CAPITA US$340
CLIMATE Tropical in south, temperate in north; monsoons June to September
HIGHEST POINT Kanchenjunga 8,598 m (28,208 ft)
 Editor for Asisbiz: Matthew Laird Acred
Editor for Asisbiz: Matthew Laird Acred
If you love our website please donate so we can make this site even better !!